Featured
Table of Contents
Can I Use A Vpn With Tor?
In practice, Tor Internet browser is free, while VPNs are typically paid, which makes your choice easy? You must simply opt for Tor and call it a day. Well,? Today, I want to provide you a full contrast of Tor vs VPN and discuss what they represent, their distinctions, use cases, and a lot more.
To start this Tor vs VPN contrast, I first need to explain what these tools represent. Besides, offering you a clear meaning of what they are and how they work will help you understand their differences, so pay close attention. Beginning with Tor, this term is an abbreviation for "The Onion Router".
Nord, VPN It's crucial to keep in mind that this is a tool for privacy and not privacy I'll discuss why quickly. When it comes to Tor nodes, they're held and preserved by volunteers, so we're talking about a decentralized service, rather than a central service which holds true with a VPN.
The silver lining is privacy because nodes aren't run by any particular companies, so you aren't running the risk of saving and logging your surfing activity by that business. On the other hand, the security of each node depends on the person that's keeping it. As such, a node can be jeopardized by a hacker, let's say, who will have the ability to trace your connection.
Tor Vs. Vpn - What's The Difference?
The entry node is more critical due to the fact that, when connecting to Tor, your ISP can see that you did that through the entry node. That's why many individuals utilize a VPN with Tor to encrypt their connection and prevent the ISP from seeing their Tor use. We'll speak about that later in this Tor vs VPN post.
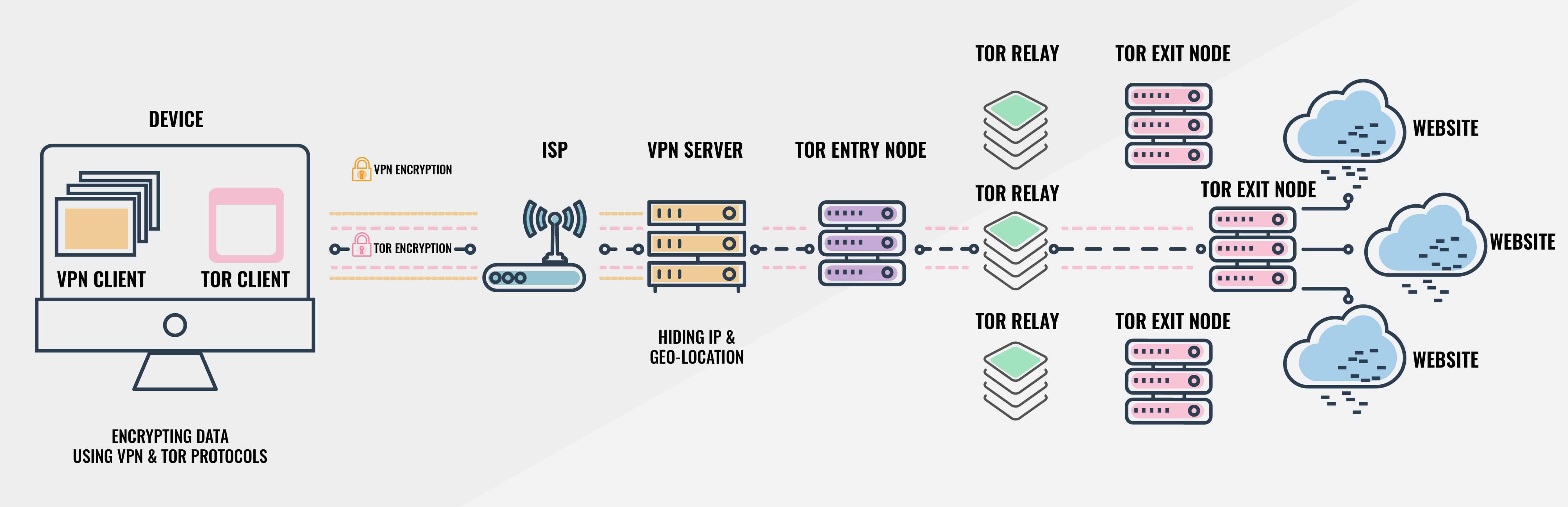
Its "The Onion Router" name comes from the truth that it peels the layers of encryption similarly to the onion layers. And dark web websites also have the domain ". onion", which isn't a coincidence. Listed below, I explained how Tor works and the procedure of encrypting and decrypting your requests.
When you link to the Tor network and you send out a demand, you get triple file encryption for each node. There's the entry node (typically called the guard node), the middle node (or middle server), and the exit node. Tor sends your request to the entry node, which removes the very first layer of file encryption.
The entry node can't read the encrypted content of the request, so it still can't trace your activities inside the Tor network. The traffic is then sent to the middle node, which removes another layer of file encryption and sends out the encrypted traffic to the exit node. Finally, the exit node peels the last layer of encryption, which is why it can see the encrypted request but it can't recognize who is sending it since it can't see your IP address.
Vpn Vs Tor 2023 Comparison: 8 Tests, 1 Clear Winner
If you're looking to stay confidential online and you're believing about using Tor, I believe it's great to understand more about its benefits and drawbacks, so check them out listed below. The triple layer of encryption ensures 100% privacy when using Tor Web browser It's free and does not need any subscriptions It's a decentralized, open-source network with no tracking and surveillance Tor Web browser is capable of going on the dark web The entry node can read your IP address and make it noticeable to your ISP when using Tor Slows down your web speed considerably due to innovative encryption Nodes are run by volunteers who might not do a great task at making sure they're secure You can't choose an IP address from a particular nation, so you can't bypass geo-blocks Tor Web browser doesn't work on all platforms Wondering what are the differences between Tor and VPN?
VPN services provide countless servers in various nations, so they allow you to link to any of them quickly and get an IP from the country you need. Each demand you send out is routed through a VPN tunnel where it is sent to a VPN server which decrypts it and links you to the website you want.
, for example, while Tor encrypts just the part of the connection sent through the Tor Web browser.
With a single layer of file encryption, the VPN in fact goes through fewer steps to protect your connection which has a big benefit much quicker speeds and much better efficiency. Let's talk about the pros and cons of VPNs and see what they do well and what are their shortcomings. They're very easy to use VPNs can be installed on every platform (Windows, i, OS, Linux, Android, mac, OS, routers,) You can choose an IP address from a specific country, letting you bypass geo-restrictions There's a greater degree of responsibility because you understand who owns the VPN servers VPNs are extremely fast and exceptional companies provide 10 Gbps servers Advanced security features like a kill switch, ad blocker, and Multi, Hop Overall personal privacy, thanks to sophisticated file encryption and the capability to conceal your original IP It's a paid service which can be an issue for budget-constricted users Some VPN services are known for storing logs (Hola VPN, Ninja, VPN, Betternet,) You must select a trustworthy VPN that has a no-logs policy since you're turning over your privacy/anonymity to that company Now that you what Tor and VPN are, I feel the need to quickly summarize their distinctions simply to make sure you comprehend everything well.
Latest Posts
Best Virtual Private Network (Vpn) Software 2023
The Best Vpn For Business In 2023: Top 8 Corporate ...
Best Vpns For Freelancers And Remote Workers: Protect ...